Insights - BRE Group
Insights: latest thinking from BRE
Discover our latest thinking, informed by our independent research and analysis.

Insights
BRE’s 100 day roadmap for the incoming UK Government
The Labour Party’s manifesto set out an ambitious, multi-faceted plan to grow and decarbonise the UK economy.

Insights
BRE’s 100 day roadmap for the incoming UK Government

LPCB
The journey from research to test standard for video flame detectors

SmartWaste
How SmartWaste enhances Modern Methods of Construction (MMC)
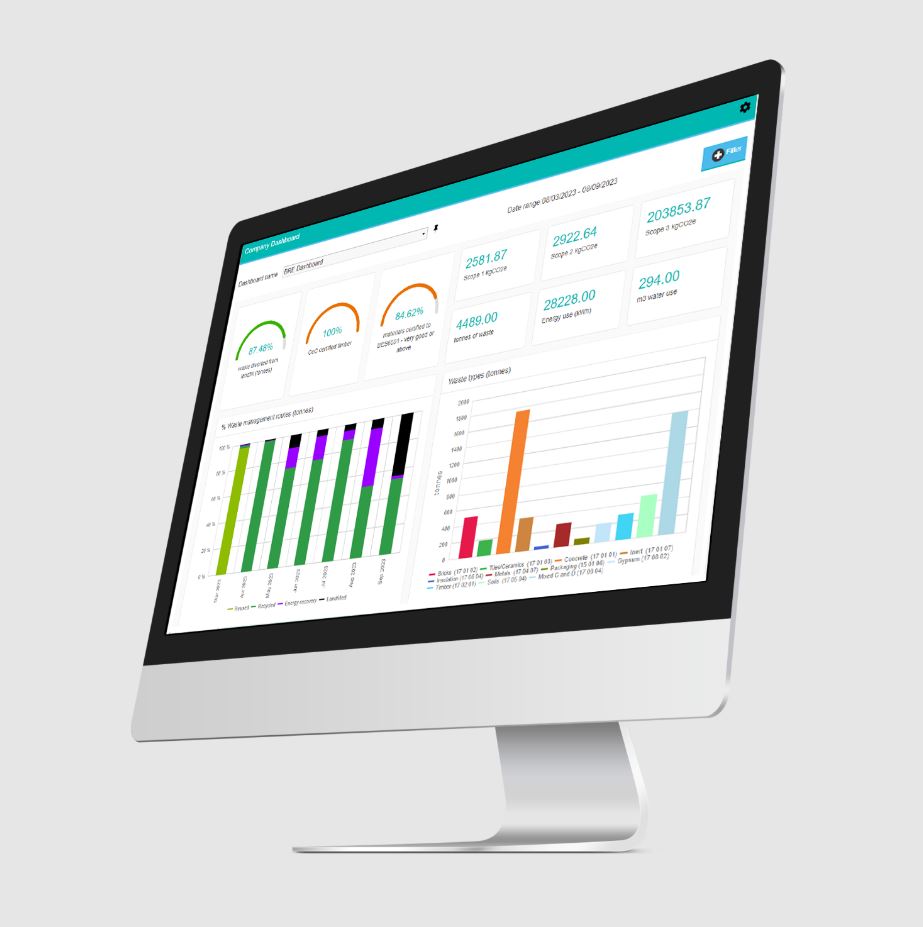
SmartWaste
SmartWaste V11: paving the way to net zero carbon and sustainability in construction

Insights
Environmental Declarations for Construction with BRE

Insights
Navigating urbanisation: a focus on better standards for indoor air quality

Insights
How to meet net zero by changing the way homes are heated

Insights
BRE's response to changes to the National Planning Policy Framework

Insights
BRE responds to the government's net zero review

Insights
What does the spring statement mean for the built environment?

Insights
How decarbonising the built environment is the key to meeting net zero

Insights
BRE’s response to the Levelling Up White Paper

Insights
BRE's CEO optimistic for 2022 following a challenging year

Insights
Fuel poverty and its impact on domestic energy consumption in England

Insights
Does the UK heat and buildings strategy go far enough?

Insights
Challenges for the built environment: an ageing population

Insights
Sustainable finance: why investors cannot afford to be left behind

Insights
Researching when optical smoke detectors and alarms should be replaced

Insights
Fire fatalities in Scotland and recommendations to help reduce them
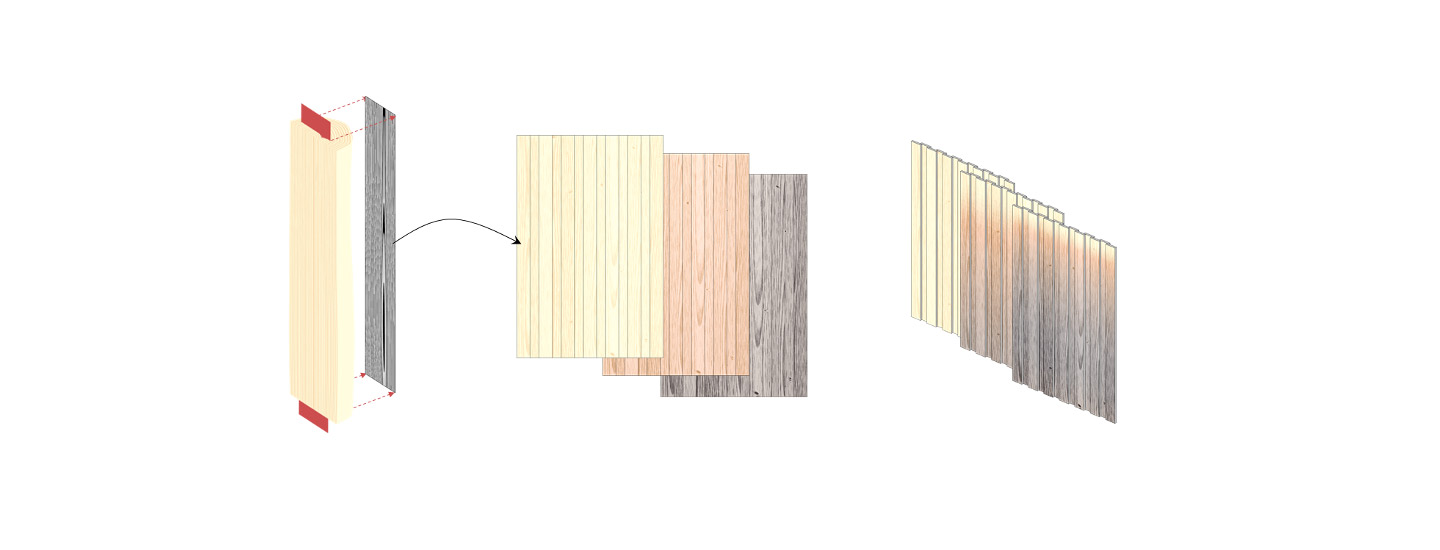
Insights
Predicting the service life of timber structures

Insights
First phase review of fire fatalities and injuries in Scotland

Insights
BRE research into the effectiveness of visual alarm devices

Fire safety testing
BRE finds new ways to test video flame and video smoke detectors

Insights
An investigation into the effectiveness of visual alarm devices

Insights
How to characterise smoke from materials and evaluate smoke detectors

Insights
BREEAM return from talks regarding further work in the Maldives

Insights
Biophilic office design: putting people's health and wellbeing first

Insights
Predictions for the future: tech and its impacts on society

Insights
Diagnosing the causes of dampness in buildings

Insights
Guidance to help combat the challenges of overheating in dwellings

Fire safety testing
New tests examine sprinkler systems on mobility scooter fires

Insights
How pre-demolition & pre-refurbishment audits aid resource efficiency

Fire safety testing
Smoke detector research to find if current tests are adequate

Insights
How to correctly identify different grades of stainless steel

Insights
Causes of false alarms and identifying measures to reduce them
Insights
Movement joints and stress relief in concrete screed to prevent cracks

Insights
BRE examine whether triple glazing is really better than double

Insights
BRE looks at the importance of holistic fire safety management

Insights
Why you should comply with Regulation 38 of the building regulations

Insights
Making multi-storey buildings exits safer in the event of a fire
Viewing 6 of 45





